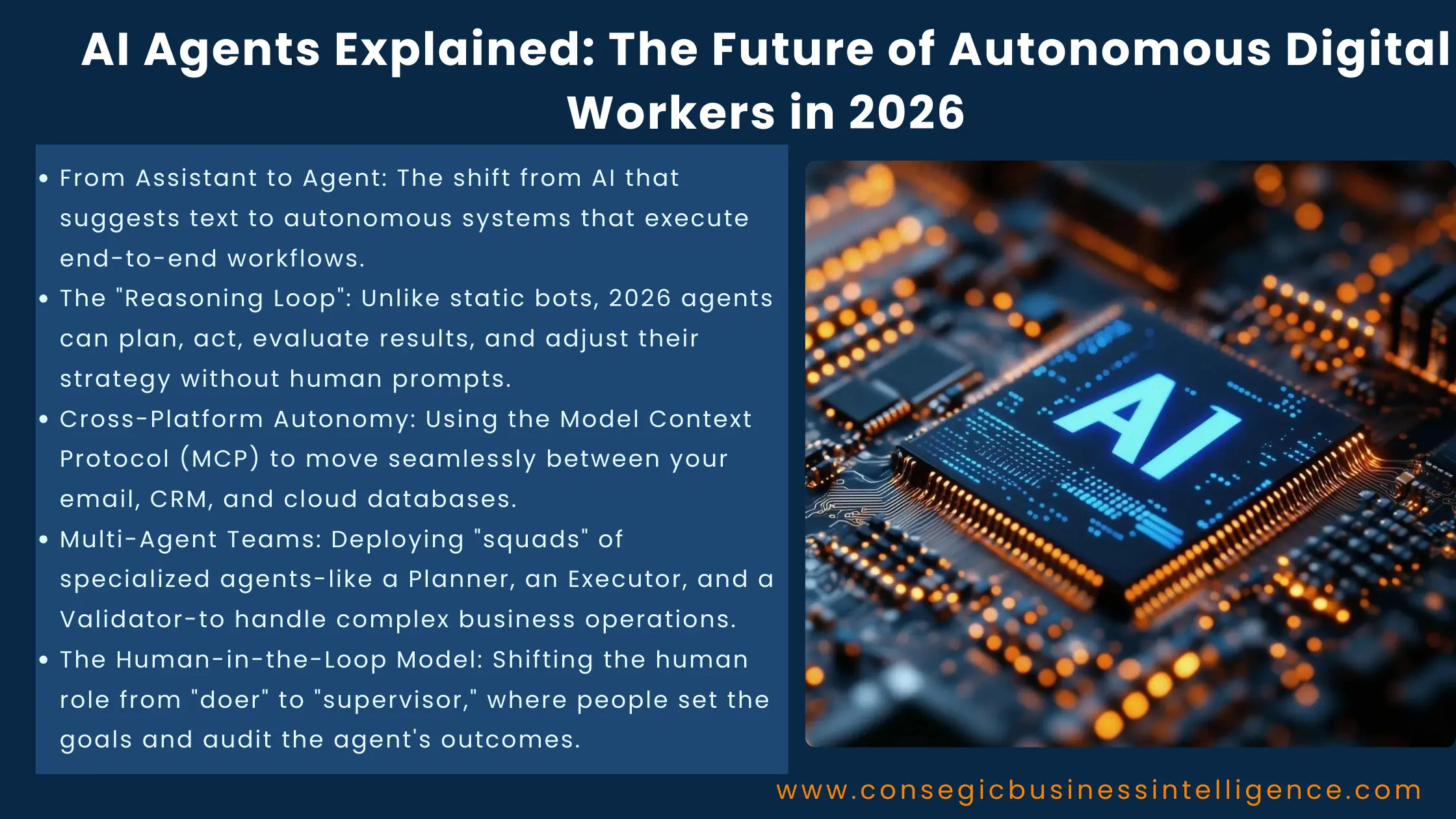
AI Agents Explained: The Future of Autonomous Digital Workers in 2026
AI Agents Explained: The Future of Autonomous Digital Workers in 2026
Artificial intelligence is no longer just a tool for answering questions or suggesting edits. In 2026, AI agents are taking a much bigger role as autonomous digital workers that can carry out tasks, make decisions, and act independently on behalf of users. These intelligent systems are becoming foundational to how businesses operate, how people work, and how everyday digital tasks are completed. Understanding AI agents and their impact helps us make sense of the future of work and technology in a world increasingly powered by autonomous software.
What Are AI Agents?
At a basic level, an AI agent is a software program that can perform actions in an environment to achieve specific goals. Unlike traditional software that follows strict rules, AI agents observe data, analyze patterns, and make decisions on their own based on objectives set by humans. These agents interact with digital systems, collect information, and determine the best steps to complete tasks without constant human intervention. This kind of autonomy makes them more capable and flexible than typical AI assistants or bots. In this context, AI agents act not just as tools, but as digital workers that can accomplish work with minimal supervision.
From Assistants to Autonomous Performers
Earlier generations of AI, such as basic chatbots or AI assistants, responded to user requests by fetching information or performing simple tasks. In 2026, AI agents are evolving into systems capable of more complex work. These modern agents can prioritize tasks, plan steps, access multiple data sources, and execute sequences of actions until a goal is complete. This means they manage workflows, rather than just complete isolated tasks. By operating independently, they free up human workers to focus on more strategic and creative work.
How AI Agents Work Behind the Scenes
AI agents combine several technologies to operate effectively. They use machine learning to process and learn from data, natural language processing to interpret requests, and decision logic to determine the next best actions. When given a task, they gather relevant information, evaluate possible steps, and choose actions that align with the desired outcome. Over time, these agents can adapt and improve their performance by learning from successes and errors, enhancing their ability to handle future tasks more effectively. This continuous learning makes them valuable assets in environments where requirements and data change frequently.
Real-World Uses of AI Agents
In 2026, AI agents are already being applied in many fields. In customer service, they help resolve user queries and guide customers through common support issues without human intervention. In business settings, they can analyze reports, manage schedules, or automate follow-up activities. In project and IT operations, some AI agents monitor systems, detect issues, and trigger corrective actions that keep workflows running smoothly. These examples show how agents can act like autonomous digital workers, completing multi-step goals based on real-time data and changing conditions.
Benefits of Autonomous Digital Workers
One of the biggest advantages of AI agents is their ability to increase productivity and efficiency. By automating routine and time-consuming tasks, these systems allow human employees to focus on higher-value work that requires creativity and judgement. AI agents can also reduce human error, improve consistency, operate around the clock without fatigue, and scale across large amounts of data. For organizations, this means faster task completion and often lower operational costs. In competitive industries, having autonomous systems handle predictable work can be a real differentiator for innovation and growth.
Collaboration Between AI Agents and Human Workers
Rather than replacing people, AI agents are expected to augment human capabilities. In many workplaces, AI agents will work alongside teams, acting like digital colleagues that take on routine responsibilities and provide recommendations. Experts suggest human and AI collaboration will become the norm in many industries, with machines handling data-intensive tasks and people focusing on decisions that require empathy, context, and strategic thinking. This hybrid approach helps ensure that human values and oversight remain central as autonomous systems grow more capable.
Challenges and Considerations for 2026
While the promise of autonomous AI is strong, it also introduces important challenges. AI agents must be designed with security and governance in mind to prevent misuse or unintended consequences. Because they can make decisions based on large amounts of data, organizations need clear policies on how these systems access and handle sensitive information. Trust and transparency are critical because users must understand how and why an AI agent makes certain decisions. These considerations will shape how companies adopt and regulate their use of autonomous digital workers.
The Future of Autonomous Digital Work
In 2026, AI agents are moving beyond novelty to become mainstream components of digital ecosystems. Their ability to operate independently, adapt to new situations, and take action on complex goals marks a significant shift in how work gets done. Experts predict that AI agents will continue advancing, integrating deeper into business systems, digital services, and everyday workflows. As they become more capable, their role as autonomous digital workers will expand, transforming the way people approach productivity, collaboration, and innovation in the digital age.
Conclusion
AI agents represent a meaningful leap in artificial intelligence technology. In 2026, these autonomous systems are becoming essential to how tasks are completed, decisions are informed, and workflows are managed. By acting as digital workers capable of independent action, AI agents are reshaping the future of work and enabling new levels of efficiency across industries. While challenges in oversight and governance remain, the potential for AI agents to enhance both business performance and human productivity is clear. As we move forward, learning to work with these systems will be key to unlocking the full benefits of AI in everyday life and enterprise operations.