Therapies and Leading Providers in the Connective Tissue Disease Market
The connective tissue disease (CTD) market is gaining global prominence due to the rising prevalence of autoimmune and inflammatory disorders that affect the body’s connective tissues, including skin, joints, muscles, and blood vessels. These diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis, and mixed connective tissue disease can cause chronic pain, organ dysfunction, and reduced quality of life.
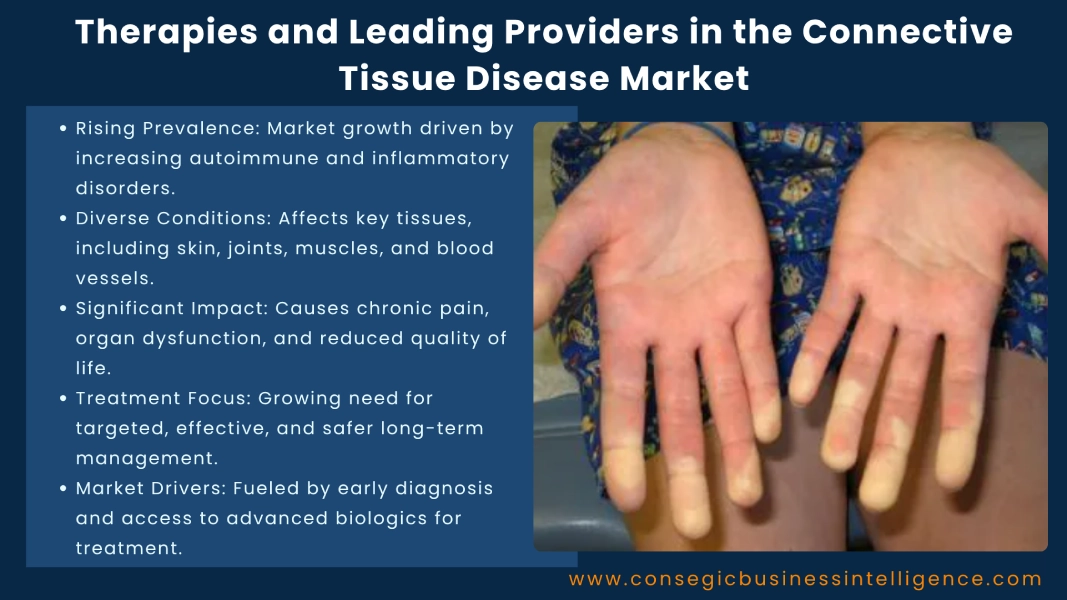
As these conditions often require long-term management, there is a growing emphasis on developing targeted, effective, and safer treatment options. The rise in autoimmune disorders, improvements in early diagnosis, and expanding access to advanced biologics are fueling the global connective tissue disease market growth.
In this Blog, we will explore the five key therapies transforming CTD treatment and the five leading providers driving innovation and accessibility in this evolving therapeutic landscape.
- Biologic Therapies: Revolutionizing Immune Modulation
Biologic therapies have redefined treatment for connective tissue diseases by targeting specific immune system components instead of broadly suppressing immunity. These therapies, made from living cells, inhibit cytokines and immune pathways responsible for inflammation and tissue damage.
Drugs such as adalimumab (Humira) by AbbVie, etanercept (Enbrel) by Amgen and Pfizer, and infliximab (Remicade) by Johnson & Johnson’s Janssen Biotech are widely prescribed for rheumatoid arthritis and lupus-related conditions.
Biologics targeting TNF-α, IL-6, and B-cell pathways have improved disease management by reducing flare-ups and slowing progression. As biosimilars expand globally, these therapies are becoming more accessible, marking a major step forward in personalized autoimmune treatment.
- Immunosuppressive and Corticosteroid-Based Treatments
Immunosuppressive drugs and corticosteroids remain the foundation of therapy for many connective tissue diseases. These medications help control overactive immune responses and relieve inflammation that damages organs and joints.
Common treatments include methotrexate, azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil, and prednisone. Companies such as Roche, Novartis, and Bristol Myers Squibb continue to provide these essential drugs globally, ensuring their widespread availability.
While corticosteroids offer rapid relief, prolonged use may lead to side effects. This has encouraged ongoing research into steroid-sparing drugs that maintain therapeutic benefits with fewer long-term risks. Despite the influx of modern biologics, these classic therapies remain critical for early and sustained disease control.
- Targeted Small Molecule Inhibitors
Small molecule inhibitors, particularly Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, have become a vital addition to CTD treatment options. These oral medications target intracellular signaling pathways involved in autoimmune inflammation, offering a convenient alternative to injectable biologics.
Notable examples include tofacitinib (Xeljanz) by Pfizer, baricitinib (Olumiant) by Eli Lilly, and upadacitinib (Rinvoq) by AbbVie. These drugs are effective in treating rheumatoid arthritis and are being explored for lupus and scleroderma management.
By regulating cytokine signaling at the cellular level, JAK inhibitors provide precise control over immune activity. Their oral administration and strong efficacy profile make them a preferred choice for patients seeking long-term, manageable therapies.
- Stem Cell and Regenerative Therapies
Stem cell therapies are gaining traction as a groundbreaking approach for treating severe or treatment-resistant connective tissue diseases. These therapies work by regenerating damaged tissues and resetting immune balance, offering potential for long-term remission.
Companies and research institutions like Mesoblast Limited, Fresenius Medical Care, and Novartis are exploring hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) and mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) therapies for conditions such as systemic sclerosis, lupus, and myositis.
Early clinical results have demonstrated improved tissue repair and immune tolerance, giving hope to patients with advanced or unresponsive CTDs. While stem cell therapy is still emerging, its potential to transform disease management is widely recognized within the medical community.
- Anti-Fibrotic and Organ-Specific Therapies
Fibrosis, or excessive tissue scarring, is a key complication in diseases like scleroderma and mixed connective tissue disorders. Anti-fibrotic therapies aim to inhibit fibroblast overactivity, reducing organ damage and improving patient outcomes.
Boehringer Ingelheim’s nintedanib (Ofev) and Roche’s pirfenidone (Esbriet) are among the leading anti-fibrotic drugs showing success in systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD). These drugs prevent further fibrotic progression, improving lung function and survival.
The growing focus on organ-targeted treatment strategies represents a shift toward more personalized and effective care, especially for patients with life-threatening connective tissue complications.
- Leading Providers in the Connective Tissue Disease Market:
As therapies evolve, several pharmaceutical leaders are at the forefront of developing, manufacturing, and commercializing advanced treatments for connective tissue diseases. These companies are driving innovation in biologics, small molecule drugs, and regenerative therapies, helping shape the future of autoimmune care.
- Roche Holding AG
Roche, headquartered in Switzerland, is a global leader in immunology and autoimmune research. The company’s flagship products including rituximab (Rituxan) and tocilizumab (Actemra) have become key treatments for rheumatoid arthritis, vasculitis, and lupus.
Roche’s ongoing focus on precision immunotherapy and antibody-based treatments continues to influence CTD drug development. Its collaboration with Genentech further strengthens its presence in the biologics market, expanding therapeutic access worldwide.
- GlaxoSmithKline plc (GSK)
GSK has made significant contributions to autoimmune disease treatment through belimumab (Benlysta), the first biologic approved specifically for systemic lupus erythematosus. The company continues to explore B-cell–targeted and cytokine-modulating therapies for various connective tissue disorders.
GSK’s research pipeline emphasizes innovation in immune pathway modulation and long-acting biologics, reinforcing its leadership in precision treatment and chronic disease management.
- AbbVie Inc.
AbbVie, based in the United States, is a pioneer in biologic and immunology-based drug development. Its adalimumab (Humira) remains one of the most widely used biologics for autoimmune conditions, including rheumatoid arthritis and lupus.
With next-generation therapies like upadacitinib (Rinvoq), AbbVie is focusing on expanding into small molecule and targeted oral therapies. The company’s diversified immunology portfolio continues to drive advancements in chronic inflammatory disease management worldwide.
- Eli Lilly and Company
Eli Lilly, headquartered in the U.S., has a strong foothold in autoimmune therapeutics through drugs like baricitinib (Olumiant), a leading JAK inhibitor. The company’s expanding pipeline includes novel cytokine blockers and T-cell modulators targeting lupus, arthritis, and related disorders.
Lilly’s approach combines data-driven clinical research and patient-centric design, ensuring that its therapies deliver both efficacy and safety. With continuous investment in immunology, Eli Lilly remains a key contributor to CTD therapeutic innovation.
- Boehringer Ingelheim
Boehringer Ingelheim, a German pharmaceutical leader, has gained prominence for its anti-fibrotic therapy nintedanib (Ofev), which has become a critical treatment for patients with systemic sclerosis-associated lung disease.
The company’s focus on fibrosis and inflammation research positions it at the forefront of developing organ-protective therapies for connective tissue diseases. Boehringer’s commitment to improving patient outcomes through precision targeting of fibrotic pathways continues to drive new advancements in CTD care.
Conclusion
The connective tissue disease market is advancing rapidly as breakthroughs in biologics, immunosuppressants, targeted therapies, and regenerative medicine reshape treatment paradigms. Leading pharmaceutical companies such as Roche, GSK, AbbVie, Eli Lilly, and Boehringer Ingelheim are driving these innovations, ensuring patients have access to more effective, personalized, and sustainable therapies.
As research deepens and diagnostic accuracy improves, the future of CTD treatment lies in precision immunology, regenerative approaches, and organ-targeted drug development. Together, these advancements promise to enhance long-term disease control, minimize complications, and significantly improve the quality of life for millions living with connective tissue disorders worldwide.