Advancements and Treatment Options in the Acute Sinusitis Market
Acute sinusitis, also known as acute rhinosinusitis, is a condition marked by inflammation of the sinuses, often triggered by viral infections and occasionally bacterial complications. Its symptoms such as nasal congestion, facial pain or pressure, headaches, and reduced sense of smell can significantly affect quality of life, even if the condition is temporary. While many cases resolve on their own, others require medical intervention, making effective treatment essential.
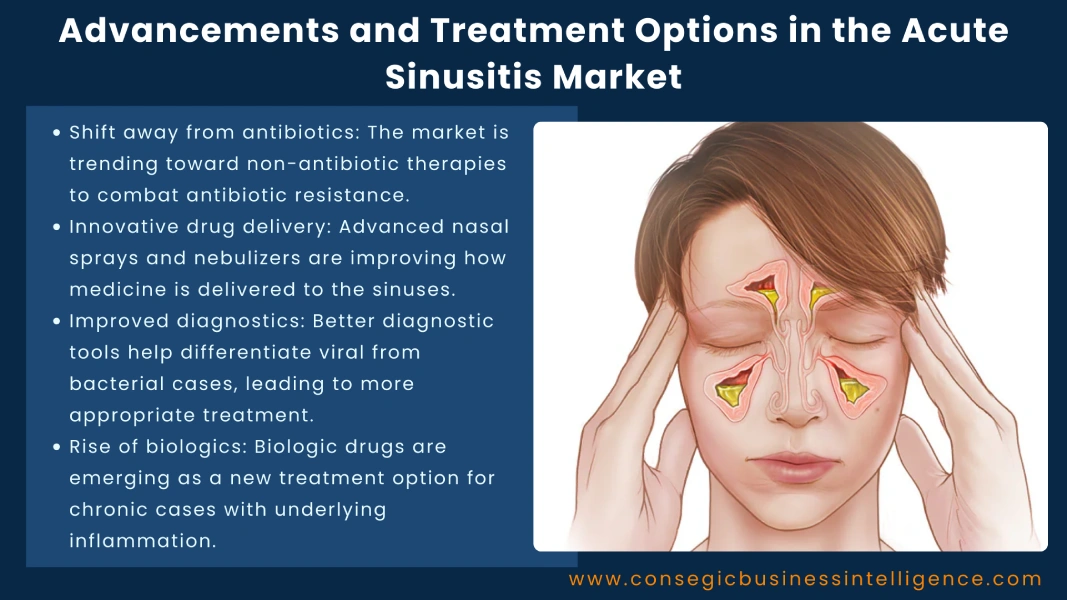
The global acute sinusitis market is evolving rapidly, driven by innovation in drug delivery, increased emphasis on non-antibiotic therapies, and advances in diagnostics. In this blog, we explore the key treatment options currently in use and the recent advancements shaping the future of this market worldwide.
Treatment Options in Acute Sinusitis
- Symptomatic and Supportive Care
The majority of acute sinusitis cases are viral and resolve naturally within one to two weeks. Moreover, supportive therapies such as saline nasal irrigation, nasal corticosteroid sprays, decongestants, analgesics, and rest remain first-line treatments. These options relieve discomfort, improve drainage, and reduce inflammation, helping patients manage symptoms effectively without unnecessary medications.
- Antibiotic Therapy
When acute sinusitis is bacterial in origin, antibiotics are prescribed. The standard choice is amoxicillin or amoxicillin/clavulanate, with alternatives for patients allergic to penicillin or in areas with high resistance rates. Treatment is usually reserved for cases lasting more than 10 days, severe infections with high fever and purulent discharge, or worsening symptoms after initial improvement. Antibiotics remain a cornerstone but must be used carefully to minimize resistance.
- Intranasal Corticosteroids and Combination Therapies
Steroid nasal sprays such as fluticasone and mometasone help reduce mucosal inflammation and accelerate recovery. These sprays are particularly effective in patients with significant swelling and nasal blockage. Newer drug-device combinations and formulations are improving penetration into hard-to-reach sinus areas, making corticosteroids more effective when used alone or with decongestants.
- Minimally Invasive Surgical Procedures
For patients who do not respond to medication or who have structural blockages, minimally invasive interventions such as balloon sinuplasty and functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) are available. Balloon sinuplasty uses a catheter and balloon to gently expand sinus openings, while FESS removes obstructing tissue under direct visualization. Both procedures improve drainage, reduce recurrence risk, and minimize recovery time compared to traditional surgery.
- Allergy Management and Immunotherapy
Allergies are a common underlying factor in recurrent sinusitis. Antihistamines, allergen avoidance strategies, and in selected cases, immunotherapy (“allergy shots”) are used to manage allergic triggers. By reducing the frequency and severity of allergic reactions, these therapies lower the risk of acute sinusitis episodes, offering long-term benefits to patients with chronic allergy-related sinus issues.
Recent Advancements and Research Trends
- Drug-Delivery Innovations
One of the most significant advancements is the development of drug-delivery devices that allow deeper penetration of steroids and other medications into sinus cavities. Exhalation delivery systems, for example, improve deposition in areas standard sprays cannot reach. These innovations reduce relapse rates, enhance efficacy, and improve overall patient outcomes.
- Non-Antibiotic and Microbiome-Based Therapies
Concerns about antibiotic resistance have accelerated the exploration of alternative therapies. Research is focusing on microbiome modulation, probiotics, and immunotherapies to restore balance in sinus flora. Non-antibiotic treatments aim to control infection and inflammation while preserving microbial health, reducing recurrence, and minimizing risks associated with long-term antibiotic use.
- Advanced Diagnostic Tools and Digital Health
Improving diagnostic accuracy is another key area of advancement. New technologies help distinguish viral from bacterial sinusitis more reliably, reducing unnecessary antibiotic prescriptions. Artificial intelligence in imaging, telemedicine consultations, and digital symptom-tracking tools are making diagnosis more accessible and precise, particularly in remote or underserved areas.
- Shorter Antibiotic Courses and Optimized Guidelines
Updated clinical guidelines recommend shorter courses of antibiotics for eligible patients, typically 5 to 7 days instead of longer regimens. This change not only reduces resistance but also limits side effects and healthcare costs. “Watchful waiting” strategies are also gaining traction, where physicians delay prescribing antibiotics unless symptoms persist or worsen, aligning treatment with best-practice stewardship principles.
- Plant-Derived and Alternative Symptom Relief Agents
Herbal and plant-derived agents are gaining attention as complementary therapies. Essential oil-based formulations and phytotherapeutics have shown potential in reducing congestion, thinning mucus, and alleviating facial pain. These natural alternatives appeal to patients seeking non-synthetic treatments and provide additional tools in managing mild to moderate acute sinusitis cases.
Conclusion
The acute sinusitis market is undergoing a shift from purely symptomatic relief and broad antibiotic use to a more sophisticated, patient-centered approach. Current treatment options such as supportive care, corticosteroids, antibiotics, surgical procedures, and allergy management remain the foundation of care. At the same time, advancements in drug-delivery systems, microbiome-based therapies, digital diagnostics, optimized antibiotic use, and alternative agents are reshaping how the condition is treated worldwide.
As healthcare systems emphasize safety, efficiency, and reduced resistance, the market for acute sinusitis treatments is poised for growth. Providers that integrate these innovations into practice will not only improve outcomes but also meet the rising demand for effective, sustainable, and patient-friendly solutions.