Genetic Testing Market Size:
Genetic Testing Market size is estimated to reach over USD 61.02 Billion by 2031 from a value of USD 21.45 Billion in 2023 and is projected to grow by USD 21.57 Billion in 2024, growing at a CAGR of 14.0% from 2024 to 2031.
Genetic Testing Market Scope & Overview:
Genetic testing is a medical method through which an individual's DNA is identified via genetic variations. The variations can indicate a predisposition to health conditions, inherited diseases and traits, etc. Typically, an individual's genes taken from the blood sample, tissue sample, or saliva are tested for mutations, abnormalities, changes, etc. This form of testing identifies or rules out specific genetic conditions in chromosomes or proteins based on symptoms. This process ensures the identification of gene mutations that could be passed down to future generations. They also can ascertain the probability of developing genetic disorders prior to the appearance of any symptoms. These tests are often accurate and can help tailor treatments based on personal genetic profiles, increasing effectiveness and lowering side effects. The end-users of this method are the healthcare sector, forensics, pharmaceutical and agriculture industry, and consumer genetics study.
How is AI Transforming the Genetic Testing Market?
AI is increasingly being integrated into the genetic testing sector to facilitate faster and more accurate diagnosis of diseases, particularly rare ones, by analyzing vast genomic data to identify disease patterns and biomarkers. It accelerates drug discovery and development of personalized therapies tailored to an individual's genetic makeup, while also improving the understanding of complex genetic disorders. Moreover, AI-powered systems can match facial phenotypes to genetic conditions and identify genetic mutations to guide targeted treatments. In addition, AI-powered solutions can accelerate the identification of novel gene-disease associations and potential drug candidates, considerably reducing the time and cost associated with traditional drug discovery. Consequently, the above factors are projected to boost the market growth in upcoming years.
Genetic Testing Market Insights:
Genetic Testing Market Dynamics - (DRO) :
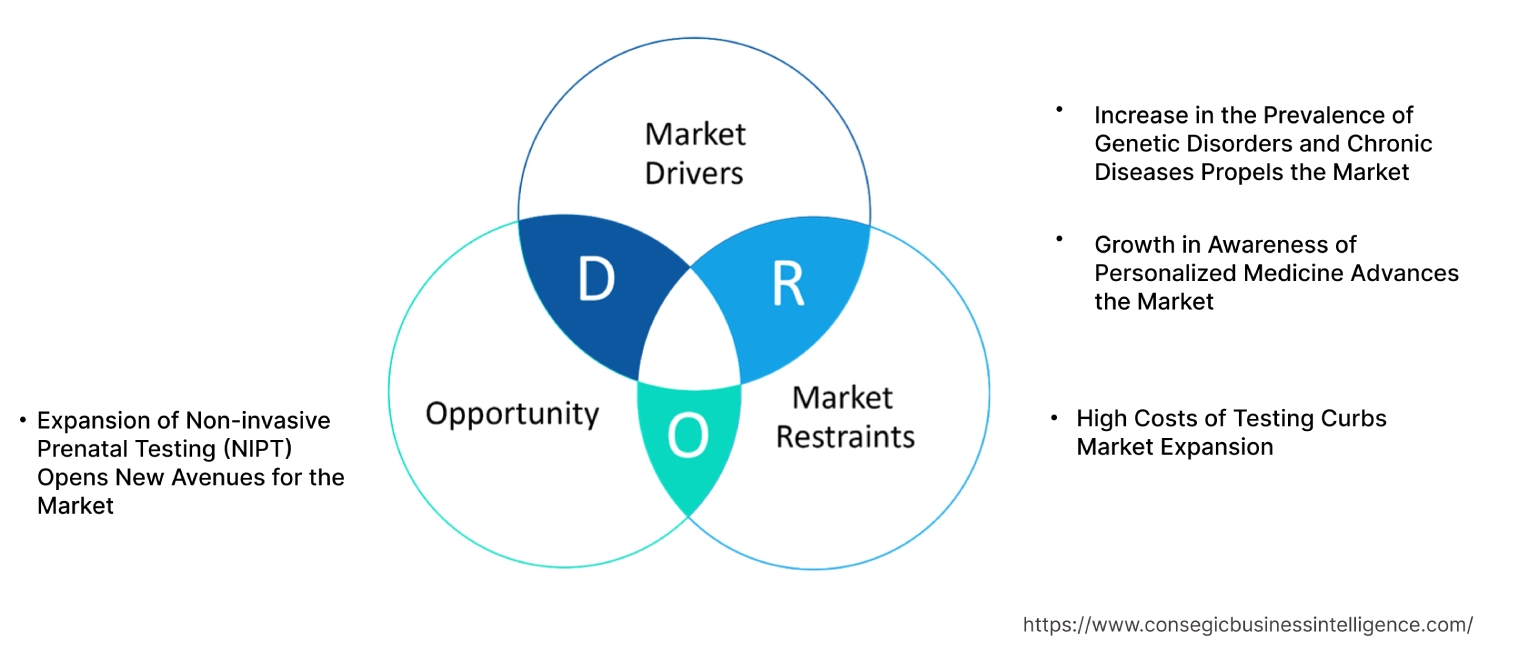
Key Drivers:
Increase in the Prevalence of Genetic Disorders and Chronic Diseases Propels the Market
As genetic diseases such as diabetes, neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular conditions, cancer, etc. rise, the need for early detection and curated medicines also rises. Genetic testing allows for the determination of genetic mutation or predisposition which could help in targeted prevention and lifestyle changes. There is also a growth of awareness about the genetic links to chronic diseases such as Huntington's disease or cystic fibrosis. The popularity of direct-to-consumer (DTC) tests for health-related insights is driving the genetic testing market growth as consumers show interest in learning about their ancestral roots. This results in a better assessment of diseases and the risks they pose.
- In 2023, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) gave its approval for using blood tests for the identification of inherited diseases that have the risk of escalating into cancer. The test was performed on September 29th, by the Invitae Common Hereditary Cancers Panel. They studied individual blood samples for 47 genes that have the probability of inheriting cancer.
Thus, this testing is becoming more accessible through technological advancements, such as next-generation sequencing (NGS).
Growth in Awareness of Personalized Medicine Advances the Market
Personalized medicines aim to curate healthcare based on an individual's lifestyle, environment, and most importantly, genetic makeup. This approach to modern healthcare seeks genetic testing to optimize patient treatment charts, specifically for high-risk diseases such as cancer, heart ailments, etc. Through these tests, pharmacogenomics understands the reaction of individual patients to particular drugs. This allows for more efficient clinical trials and drug development. Personalizing medicine can also help in proactive and preventive DTC genetic tests, allowing individuals to be more vigilant about healthcare and prevent further deterioration of critical conditions.
- In 2024 a new type of genetic testing emerged that could determine the likelihood of a drug working on an individual patient. The PGx Tests can identify gene variants that cipher drug-metabolizing enzymes within patients.
Therefore, the genetic testing market expansion is highly dependent on patient education and the adoption of personalized medicines.
Key Restraints :
High Costs of Testing Curbs Market Expansion
Genetic testing requires state-of-the-art technology, which means its affordability is not consumer-friendly. These tests can cost anywhere from a couple hundred to thousands of dollars and often are not included in insurance. This results in less eager adoption by individuals, reducing the overall demand for this medical process. Healthcare providers with limited infrastructure development opportunities cannot afford the high-quality equipment that is involved in maintaining the accuracy of testing. This process also often requires expert interpretation and follow-up counseling. This often leads to additional expenditure, hiking up the overall price of testing procedures. This results in the adoption of alternative processes like blood tests such as DNA sequencing, complete blood count (CBC) tests, imaging tests, biopsies, electrocardiograms (ECGs), endoscopy, etc.
- For instance, DNA sequencing is a fast and rapidly growing alternative to genetic testing in order to determine have timely detection of rare diseases. In 2022, a group of researchers from Standford Medicine developed a new DNA sequencing method that can deliver accurate results in just a little over 5 hours. This new genome sequencing process is often integrated with computing and cloud storage to offer enhanced diagnosis of diseases.
Therefore, as this type of testing demands high upfront charges due to unequal socioeconomic and geographic barriers its expansion is often restricted.
Future Opportunities :
Expansion of Non-invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) Opens New Avenues for the Market
Non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) is a screening process employed during pregnancy in order to identify possible genetic conditions in the fetus. Since it only requires testing an individual's blood sample, it is non-invasive and a safe method. Primarily, NIPT was used to identify chromosomal abnormalities only, however, it now can identify various genetic disorders such as microdeletions. NIPT also detects conditions such as Down syndrome, Patau syndrome, Edwards syndrome, etc. This is a fast process, with great precision rates, and can provide personalized care for the mothers.
- In vitro fertilization (IVF) genetic testing is being promoted as a way to select a healthy embryo , ushering in a new era of genetically designed babies. This would allow for more parental autonomy in making decisions for their reproductive cycle. The parents can determine their own likelihood of developing chronic diseases and their probability of passing the disease down to their offspring.
Thus, as the NIPT market growth is evident, the market finds itself with a greater opportunity to expand its influence on the global stage.
Genetic Testing Market Segmental Analysis :
By Type:
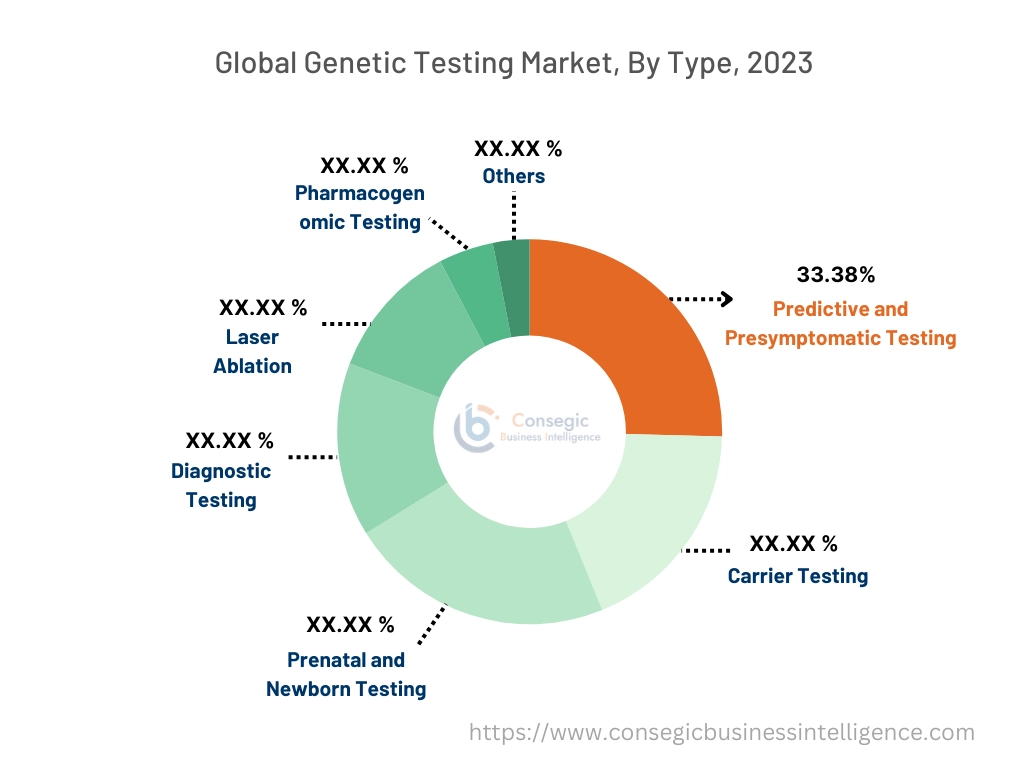
The market is segmented based on type into Predictive and Presymptomatic Testing, Carrier Testing, Prenatal and Newborn Testing, Diagnostic Testing, Pharmacogenomic Testing, and others.
Trends in the Material Type:
- This type of testing has recently allowed the development of gene therapies that aim to rectify mutations responsible for genetic diseases.
- Genetic testing is allowing for the development of RNA-based vaccines. This would affect diseases that currently have no preventive vaccines, such as AIDs.
Predictive and Presymptomatic Testing accounted for the largest revenue of 33.38% of the global genetic testing market in 2023.
- Predictive and presymptomatic testing allows for quicker resolution of genetic predispositions. This allows patients to manage their health strategies for optimum results in case of diseases such as cancer or cardiovascular disorders.
- Enhancements in genetic sequencing result in more precise, accessible, and cost-effective reports.
- The rise in awareness about early detection benefits in conditions like breast cancer is providing individuals with preventive long-term measures.
- Certain companies like 23andMe, have DTC testing which enables the detection of ancestral roots of health risks that enable individuals access to personalized care.
- For instance, in June 2024, the American Heart Association gave a statement that suggested the employment of CYP2C19 genetic testing while prescribing oral inhibitor therapy. This would prevent blood clotting which is a major contributor to heart attacks.
- Therefore, as per the genetic testing market analysis, predictive and presymptomatic testing is covered in many insurance policies making it widely.
Pharmacogenomic Testing is expected to have the fastest CAGR during the forecasted period.
- Pharmacogenomic testing allows for the curation of more accurate drug therapies based on genetic build resulting in the efficacy of treatment procedures.
- Adverse drug reactions (ADRs) are a common occurrence in the healthcare department and often result in heightened side effects and even death in some cases. This testing offers true identification of genetic biomarkers that can detect an individual's reaction to a drug.
- Integration of pharmacogenomic data in electronic health records (EHR) offers quick interpretation and analysis of genetic diseases. This allows for more efficient prescribing of medications.
- It plays an important role during cancer treatment by guiding chemotherapy and targeted therapies.
- For instance, prostate cancer (PC) has high mortality rates. This can be addressed by medicinal precision through pharmacogenomic testing (PGx) by curating therapies based on genetic data. The genetic variants that can identify drug metabolism and individual response lead to treatments that are accurate and have fewer ADRs.
- Thus, the streamlining of genetic information for accurate clinical decision-making is instrumental for proper diagnosis. This will lead to the expansion of pharmacogenomic testing thus in turn driving the genetic testing market trends.
By Technology:
The market is segmented based on technology into Cytogenetic Testing, Biochemical Testing, Molecular Testing, Fluorescent in Situ Hybridization (FISH), and others.
Trends in the Technology:
- The emergence of single-cell sequencing or artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing genetic testing through rapid analysis of genetic mutations.
- CRISPR-Cas9 is a gene-editing technology that allows accurate changes in blood sequences making it instrumental in the treatment of sickle cell anemia or beta-thalassemia.
Molecular Testing (NGS, PCR) accounted for the largest revenue of the total genetic testing market share in 2023.
- Molecular testing allows for complete sequencing of targeted areas with efficiency and high precision, resulting in faster diagnosis of complex genetic conditions.
- Molecular testing is used for cancer screening, reproductive health monitoring, and identification of rare genetic conditions. This allows for more personalized medicine development and versatility, leading to wider adoption in the healthcare industry.
- Regulatory approvals by the government for molecular testing in the detection of specific conditions like neurodegenerative diseases have driven market demand.
- Molecular testing is important in detecting genetic mutations that pose a risk, and influence drug response and therapy outcomes.
- In 2024, a novel portable molecular testing device was launched by an NGO, FIND, with the aim of achieving laboratory levels of precision for isolated locations. The new product, GeneXpert Omni which is less than 23cm and under 1kg in weight has the potential to offer high-quality cartridge tests.
- Thus, molecular testing has gained a dominant hand due to its efficiency in the detection of diseases like cardiovascular conditions or cancer.
Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) is expected to have the fastest CAGR in during the forecasted period.
- Next-generation sequencing (NGS) enables the rapid detection of mutations and disease susceptibility. This allows for the curation of better treatment strategies by healthcare professionals.
- Advancements in sequencing platforms such as the introduction of new bioinformatics tools, automation, etc, have made NGS mode effective. This also allows tests to be less expensive, thus leading to its growth.
- NGS is instrumental in non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) that employs blood sample detection methods to identify genetic abnormalities or biomarkers for cancer.
- For instance, researchers from Otto-von-Guericke University have been developing enhanced NGS strategies to cure rare mosaic diseases. NGS is dependable and can be applied to obtain DNA samples from different sources such as urine sediments, fibroblasts, etc.
- Therefore, as the healthcare infrastructure is enhancing globally, NGS is set to drive the genetic testing market opportunities.
By Application:
The market is segmented based on application into Oncology, Cardiovascular Diseases, Neurological Diseases, Infectious Diseases, and others.
Trends in the Application:
- The introduction of serial genetic testing is gaining traction as it helps new insights into a patient's conditions.
- A recent development, chromosomal microarray analysis, leads to the identification of numerical abnormalities and chromosomal structures and offers a better prognosis.
Oncology accounted for the largest revenue share in the genetic testing market share in 2023.
- Cancer has the highest mortality rate, globally. Genetic testing is a crucial avenue in oncology to identify hereditary cancer risks resulting in early diagnosis and treatment.
- This sector has benefited from the development of personalized medicines and curated therapies for individual patients due to this testing.
- For treatments in certain areas such as breast cancer (BRCA1/BRCA2), prostate cancer, colorectal, etc, this testing has become common.
- Companion diagnostics that are employed with targeted treatments rely on this testing for proper identification of biomarkers that lead to the development of cancerous cells.
- For instance, combined research conducted by the Wellcome Sanger Institute, Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Trust, Great Ormond Street Hospital, and the University of Cambridge highlights the use of whole genome sequencing in detecting cancer in children. This single-cell sequencing technique allows proper analysis of information about tumors in individual children. It results in proper clinical care and management for the children such as regular screening.
- Thus, there is a growth in public awareness and support of the government in adopting this testing in oncology. This results in the segment's contribution to generating the largest revenue share.
Neurological Diseases are expected to have the fastest CAGR during the forecasted period.
- Neurological diseases such as Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis (MS), amyotrophic sclerosis (ALS), Alzheimer's disease, etc can be easily identified among the aging population by genetic testing.
- This type of testing allows for accurate identification of genetic markers associated with neurological diseases. It can also identify the onset of neurological diseases.
- Personalized medicines can improve neurological diseases greatly. This testing provides for more provisions for specific therapies to alleviate neurological diseases.
- Conventional treatments provide neurological therapies in later stages which often results in ineffective outcomes. This testing allows for early diagnosis and results in favorable outcomes.
- For instance, researchers from Rice University have improved a non-invasive method to monitor genetic dynamics in the brain. It is aimed to understand brain development such as cognitive functioning and neurological diseases.
- Therefore, neurological diseases benefit from these testing technologies such as the NGS method for accurate identification of genetic mutations. This drives the genetic testing market trends.
By End-User:
The market is segmented based on end-users into Hospitals and Clinics, Diagnostic Laboratories, Academic & Research Institutions, Direct-to-Consumer Services, and others.
Trends in the End-User:
- The evolution of telehealth visits is reshaping the genetic testing procedure as it brings the provision of identifying genetic diseases from the comforts of a patient's home.
- The introduction of portable and point-of-care (POC) genetic testing devices is making these tests more accessible to a wider range of consumers.
Diagnostic Laboratories accounted for the largest revenue in 2023.
- The implementation of genetic testing in the identification of various disorders, prenatal screening, and curating of personalized treatment strategies in diagnostic tests, have driven the demand for diagnostic laboratories.
- The infrastructure of diagnostic laboratories is heavily advanced with technologies such as NGS, PCR, microarrays, etc. This offers more accurate tests leading to an increase in precise outcomes.
- Diagnostic laboratories offer various modes of testing, from simple carrier testing to complex genome sequencing.
- Thus, diagnostic laboratories provide a more optimal situation for testing, thus in turn boosting the genetic testing market demand.
Direct-to-consumer services are expected to have the fastest CAGR during the forecasted period.
- As patients are getting more aware of the benefits of insights into their ancestral genealogy charts, the health risks they pose, and the probable treatment, they are leaning more towards Direct-to-consumer (DTC).
- DTC genetic tests are highly convenient as test kits are easily available online. Consumers can perform the tests at home by taking a sample of saliva without relying on a clinical lab.
- DTC is an affordable way of interpreting genetic data and choosing more accurate therapies based on the informational output.
- The pandemic COVIS-19 has driven home tests as a major solution to identify hereditary illness, boosting DTC testing's utility.
- For instance, 23 and Me offers DTC testing kits to their patients. They have three variations of the testing kits, and it help consumers learn about genetic ancestry. These kits are FDA-approved and draw analysis from both paternal and maternal lines.
- Therefore, as DTC offers regulatory welfare and access to genetic information without strict medical oversight, it has led to its fast growth.
Genetic Testing Market Regional Analysis:
The regions covered are North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, the Middle East and Africa, and Latin America.
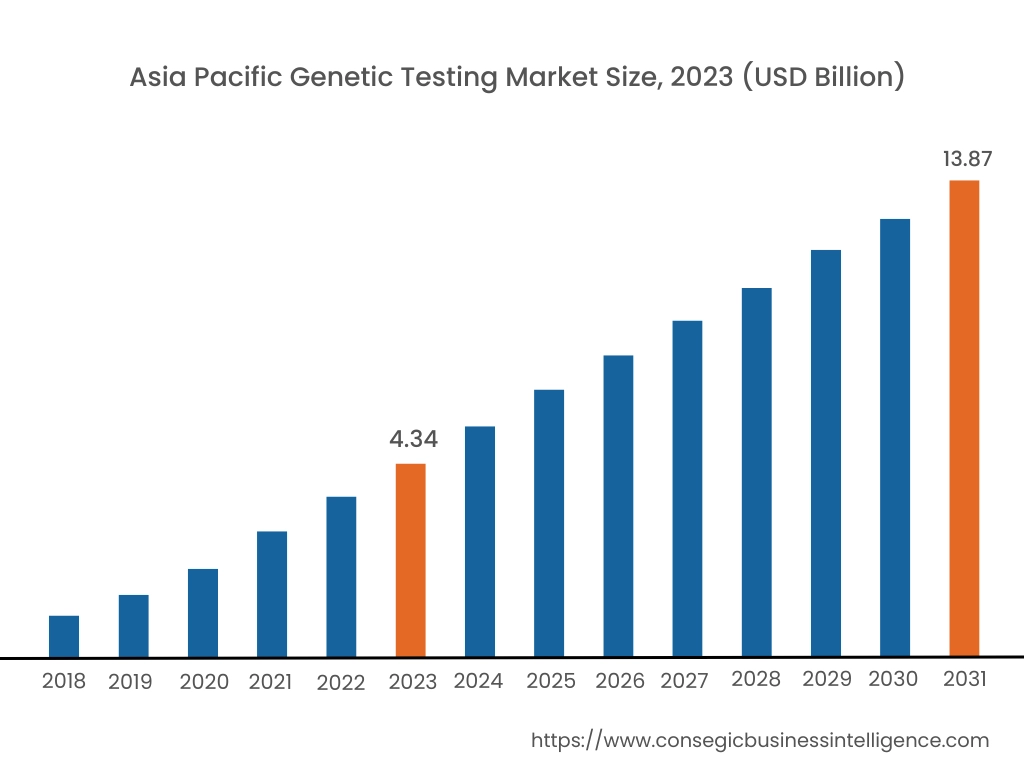
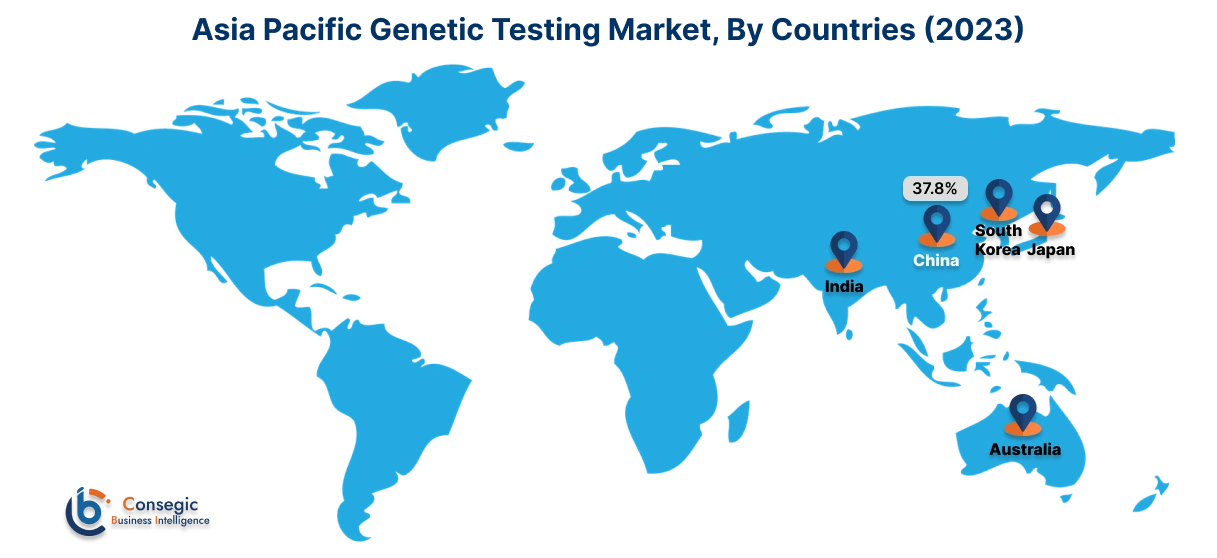
Asia Pacific region was valued at USD 4.34 Billion in 2023. Moreover, it is projected to grow by USD 4.41 Billion in 2024 and reach over USD 13.87 Billion by 2031. Out of this, China accounted for the maximum revenue share of 37.8%.
The Asia Pacific (APAC) region, especially in nations like India, China, Thailand, Vietnam, etc. has a large and genetically diverse population. This raises the probability of chronic and rare genetic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, etc. among the public. This drives the need for testing in the APAC region, leading to genetic testing market expansion.
- For instance, according to a report, the rate of breast cancer is high in the APAC region, especially in India, Indonesia, Malaysia, etc. The World Health Organization (WHO) aims to address the growing mortality rate from breast cancer in the APAC region and lower it.
North America is estimated to reach over USD 25.50 Billion by 2031 from a value of USD 9.02 Billion in 2023 and is projected to grow by USD 9.06 Billion in 2024.
The genetic testing market analysis shows that in North America, especially in the United States and Canada, there is a high concentration of skilled and developed medical infrastructure. The cutting-edge medical facilities offer an opportunity to integrate testing into daily medical care. There is an effort made by both the government and private sectors to invest in biotech, genomics, etc.
- In February 2024, Microsoft announced a partnership with 1910 Genetics, a biotech company. They would collaborate in developing a robust and AI algorithm-driven drug discovery and advancement platform. It would bring a new era of pharmaceutical research and development, resulting in the acceleration of clinical trials.
Europe has experienced a rising trend in consumer awareness about the potential health benefits of personalized medicines and pharmacogenomics. This has made this testing widely popular in many European nations, especially in the UK, Germany, etc.
In the Middle East and Africa (MEA), consanguineous marriages are prevalent. This has led to an increase in the incidence of inherited genetic disorders from parents to offspring, leading to a demand for genetic screening and counseling.
Within certain countries in Latin America, especially Brazil, Argentina, Mexico, etc DTC testing is popular as tracing ancestral roots is a personal trend. This has led to increased rates of early detection of diseases, driving the genetic testing market demand.
Top Key Players & Market Share Insights:
The genetic testing market is highly competitive with major players providing products and services to the national and international markets. Key players are adopting several strategies in research and development (R&D), product innovation, and end-user launches to hold a strong position in the genetic testing market. Key players in the global genetic testing industry include:
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (USA)
- Myriad Genetics, Inc. (USA)
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd (Switzerland)
- Illumina, Inc. (USA)
- Natera, Inc. (USA)
- QIAGEN (Germany)
- LabCorp Genetics, Inc.(USA)
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. (USA)
- Agilent Technologies, Inc. (USA)
- 23andMe, Inc. (USA)
Recent Industry Developments :
Product Launches:
- In May 2024, Latus Bio, a biotech company announced the launch of a new gene therapy technique for neurological disorders. They also announced the launch of two lead product candidates for CLN2 disease and Huntington's disease.
Mergers and Acquisitions:
- In Feb 2024, Myriad Genetics announced its completion of acquiring Intermountain Precision Genomics. Myriad is a renowned company in the market while Intermountain Precision Genomics, a branch of Intermountain Healthcare specializes in advancing personalized medicines for cancer research and treatment. Myriad acquired assets such as Precise Tumor Test, Precise Liquid Test, and Laboratory. With this acquisition, Myriad expanded its tumor profiling, boosting its oncology range.
- In August 2024, LabCorp announced the finalization of its acquisition of certain assets of Invitae. LabCorp is an ingenious and comprehensive laboratory that aids pharmaceutical companies, doctors, researchers, hospitals, etc. Invitae is a medical genetics company. The acquisition of OTC: NVTAQ would enable LabCorp to offer customized diagnostics and employ genetic analysis to enhance research and therapy plans for rare diseases and cancer.
Product Enhancements:
- In July 2024, researchers from Johns Hopkins developed new types of blood tests for neurological and psychiatric disorders. They utilized maternal blood and clinically grown brain cells to evolve the new test which can be specifically used to identify postpartum depression.
Partnerships and Collaborations:
- In June 2024, Roche announced its partnership with Ascidian Therapeutics for the advancement of gene therapies. Roche is a Swiss drug-making company while Ascidian is a biotech company. The collaboration is aimed at developing RNA exon editing therapeutics. It would target neurological diseases.
Genetic Testing Market Report Insights :
| Report Attributes | Report Details |
| Study Timeline | 2018-2031 |
| Market Size in 2031 | USD 61.02 Billion |
| CAGR (2024-2031) | 14.0% |
| By Type |
|
| By Technology |
|
| By Application |
|
| By End-User |
|
| By Region |
|
| Key Players |
|
| North America | U.S. Canada Mexico |
| Europe | U.K. Germany France Spain Italy Russia Benelux Rest of Europe |
| APAC | China South Korea Japan India Australia ASEAN Rest of Asia-Pacific |
| Middle East and Africa | GCC Turkey South Africa Rest of MEA |
| LATAM | Brazil Argentina Chile Rest of LATAM |
| Report Coverage |
|
Key Questions Answered in the Report
Who are the major players in the genetic testing market? +
The major players in the market include Illumina, Inc. (USA), Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. (USA), Myriad Genetics, Inc. (USA), F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd (Switzerland), QIAGEN (Germany), LabCorp Genetics, Inc. (USA), Natera, Inc. (USA), Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc. (USA), Agilent Technologies, Inc. (USA), and 23andMe, Inc. (USA).
What specific segmentation details are covered in the genetic testing market report? +
The genetic testing market is segmented based on type, technology, application, and end-user industry.
Which is the fastest-growing region in the genetic testing market? +
Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region in the genetic testing market.